So I was converting DV videos in Virtual Dub and I was exporting them as XviD MPEG4 in .avi format.
I'm trying to understand exactly what all of these characteristics mean for the video itself. For instance, .avi is just the container file, I know this. But I'm not sure I understand the distinction between XviD and MPEG-4 in this case. My assumption was that MPEG-4 was the compression scheme and that it was put into "another container" by way of XviD, but what exactly is the difference between XviD MPEG-4 and something like MPEG-4 Quicktime or x264?
Try StreamFab Downloader and download from Netflix, Amazon, Youtube! Or Try DVDFab and copy Blu-rays! or rip iTunes movies!
+ Reply to Thread
Results 1 to 10 of 10
Thread
-
-
mpeg-4 is a broad category that encompasses about 30 different things
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mpeg-4
xvid and divx are implementations of mpeg-4 part2 or ASP (advanced simple profile)
x264 is an encoder, and implementation of h.264 AVC (advanced video codec) or mpeg-4 part 10 -
So what exactly is digital video "made of" in regards to all these different things (not 0s and 1s, I mean)?
-
I'm not sure what you are asking? Can you clarify?Originally Posted by CursedLemon
-
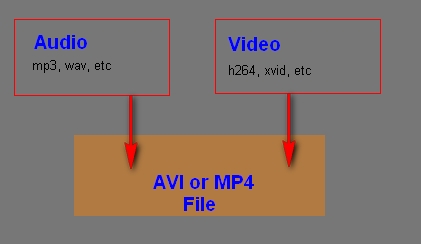
avi is the container for a video codec (xVID in your example) and an audio codec.
another popular container is mp4
avi or mp4 containers do not describe the codecs used.
A codec in its simplest explanation compresses your video. And although you do not want to hear it, digital is just 1's and 0's. -
A handy app that will help understanding video files is MediaInfo.
When you run MediaInfo on a file, it tells you the container (which is usually denoted by a file extension like .avi, .mkv, .mp4...). It also tells you what's in the container, like the video bitstream and its codec (h.264, DivX, Xvid...), and also the audio file information (MP3, AAC, AC3, DTS). You can also discover if there are other attachments in the container, like subtitles, chapters, and even extra audio tracks (other languages/mixes).
So simply, you have a container, and inside you have the audio, video, and attachments... does this help? -
I think I made the mistake of assuming that "MPEG-4" was an actual characteristic of the video data itself, instead of a broad collection of codecs LIKE XviD and x264. I think I asked the wrong question.Originally Posted by poisondeathray

-
Yeah, I think I overcomplicated it.Originally Posted by porfitron
So MPEG4 is a collection of compression schemes that SPECIFIES, for example, XviD? -
To clarify:
Container formats contain ONLY streams of data (...and header with descriptions, and formatting/partitioning of the data). This usually includes an elementary Video stream and/or an elementary Audio stream. It can also contain MORE than one of the above. It can also contain Auxiliary data streams. These might be closed-captioning, subtitle, other text data, chapter markers, possibly pictures or other menu info, maybe even Midi and http link data. Auxiliary streams are not that common, except they're a little more common in Quicktime. The container is the sheath.
Container formats:
AVI (a RIFF format)
Quicktime
Windows Media/ASF
MXF
MKV
MPG1 System Streams
MPG2 Program and/or Transport Streams
MPG4 (based on Quicktime)
Realvideo
Flash
WAV (also a RIFF format, but not supporting video streams)
some others
Elementary Video and Audio streams can contain uncompressed data or compressed data (which itself can be losslessly compressed or lossily compressed). The data is compressed by the ENCODING portion of a codec (program) when streamed/saved/stored. It is de-compressed back into uncompressed format by the DECODING portion of (usually) the same codec when played/viewed & heard/displayed/being edited. Codecs are programs with algorithms/formulas for their compression style. The codec is NOT contained in any of the streams, just a designator or description of WHAT KIND OF CODEC WAS USED to encode and OUGHT TO BE USED to decode. These have to be installed on devices correctly before the streams can be correctly used. The elementary streams are the interwoven strands. Sometimes elementary streams are seen "RAW" or outside of a container.
Types of elementary video streams:
RGB planar
4:4:4 YUV planar
4:2:2 VYUY
4:1:1 YV12
HUFFYUV
Lagarith
DV
MJPEG
Cinepak
MPEG1 CIF
MPEG2 MP@ML
MPEG2 SP@ML
MPEG4 SP@ML
MPEG4 ASP@ML
MPEG4 h.264
DivX (a type of MPEG4 ASP)
Xvid (another type of MPEG4 ASP)
WMV9 (a proprietary variant of MPEG4 ASP)
...MANY, MANY others
Types of elementary Audio streams:
LPCM
ADPCM
muLaw
aLaw
Flac
Mpeg Layer1
Mpeg Layer2
Mpeg Layer3 Backward-compatible (aka MP3)
Mpeg Layer3 Non-Backward compatible (aka AAC/A52/M4A)
AC3
DTS
...MANY, MANY others
Scott -
Think of the MP4 or AVI or MKV container as an envelope in which you place your audio and video. The audio and video can be of many different types. In addition you can place subtitles into the container, a second audio track, etc
 "Quality is cool, but don't forget... Content is King!"
"Quality is cool, but don't forget... Content is King!"
Similar Threads
-
Video Converters that supports most video formats, RM, FLV, WMV, MOV, MP4
By Baldrick in forum Video ConversionReplies: 134Last Post: 31st Mar 2021, 10:27 -
video formats
By hawkeye48 in forum Newbie / General discussionsReplies: 10Last Post: 15th Jan 2011, 09:17 -
Can someone please check out my work? ... I'll clarify...
By takearushfan in forum Newbie / General discussionsReplies: 2Last Post: 13th Jun 2010, 01:10 -
I Don't Understand video language
By capnralls in forum SubtitleReplies: 4Last Post: 29th May 2010, 10:09 -
multicamera video montage with different source fps and video formats...
By foler in forum EditingReplies: 2Last Post: 16th Feb 2009, 04:19




 Quote
Quote